This Cursor AI guide provides a deep, professional look into how developers can set up, structure, and maintain Cursor AI Rules for modern engineering workflows. Unlike basic tutorials, this guide focuses on real project setups, architecture enforcement, debugging practices, and long-term rule governance.
Cursor AI Guide: How to Set Up Your Rule System
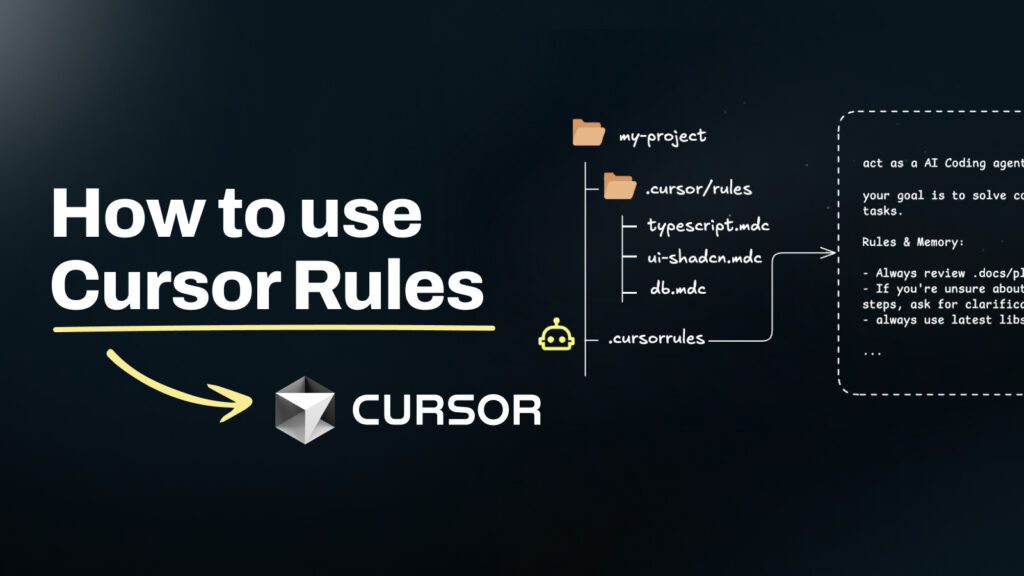
Cursor can work without rules, but teams that configure it properly experience far more consistent output and predictable behavior. Before creating your first rule, ensure your project is structured for rule-based development.
1.1 Create a Dedicated Rules Directory
Every professional project should include:
.cursor/
└── rules/Why this matters:
- Rules become version-controlled
- All contributors receive identical behavior
- PRs can include rule changes
- CI tools can validate rule files
A rules directory is foundational for scaling Cursor inside a real engineering team.
1.2 Organize Rules by Domain
Most codebases benefit from rule separation:
cursor/
└── rules/
├── core.md
├── architecture.md
├── backend.md
├── frontend.md
├── testing.md
└── security.mdThis modular structure reduces rule conflicts and ensures Cursor activates the right instruction set for each file or task.
1.3 Ensure Rules Are Indexed
Go to Settings → Indexing and confirm:
.cursor/rulesis included- Architecture docs and READMEs are indexed
- Any internal API documentation is linked
Indexed rules + indexed docs = predictable results.
Cursor AI Guide to Writing Effective Coding Rules
Most rule files fail not because the ideas are wrong, but because they are written in a human-friendly, not machine-friendly, way. The goal is clarity, not prose.
2.1 Scope Narrowly Using apply_when
Precise activation is essential. Use file globs, keywords, or patterns:
apply_when:
- file_matches: "app/services/**/*.rb"
- query_contains: ["refactor", "service object"]Narrow scoping increases rule accuracy and prevents unintended interference.
2.2 Keep Instructions Imperative and Minimal
Cursor performs best with short, direct commands:
✔ “Validate user input.”
✔ “Add tests for success and failure cases.”
✔ “Use transactions for multi-step operations.”
Avoid paragraphs, storytelling, or excessive explanation. Brevity improves reliability.
2.3 Provide Micro-Examples
Cursor learns patterns more effectively when examples are present.
# bad
User.create(params)
# good
User.create(user_params)Even a small example improves compliance dramatically.
2.4 Use Priorities to Prevent Conflicts
Assign priorities (1–100):
- 10–20 → global rules
- 30–60 → domain rules
- 100 → security or override rules
This creates a deterministic rule hierarchy.
A Practical Cursor AI Guide for Team Workflows
Rules are not documentation. They are part of your build system.
Below is the workflow mature teams follow.
3.1 Assign Rule Owners
Every rule file should have a maintainer responsible for:
- updates
- enforcement
- reviews
- resolving conflicts
This prevents fragmentation as the project grows.
3.2 Treat Rule Changes as Code Changes
All rule edits must pass through:
- pull request
- review
- visual test of generation quality
A minor rule error can influence hundreds of files — treat rules seriously.
3.3 Enforce Automatic Test Generation
Include this line in your core rule:
Always generate or update tests for new logic, refactors, or bug fixes.This turns Cursor into a test-driven system by default.
3.4 Add Architecture Enforcement Rules
You can prevent architecture decay by defining boundaries, such as:
Controllers → Services → RepositoriesCursor must respect these constraints during feature work and refactoring.
Cursor AI Guide to Debugging and Rule Troubleshooting
When a rule seems ignored, the issue is almost always scoping, priority, or clarity.
4.1 Check Whether the Rule Was Applied
Cursor’s context panel shows applied rules.
If your rule is missing:
- file path mismatch
- overly strict
apply_when - overridden by a higher-priority rule
Adjust scopes one step at a time.
4.2 Simplify Before Expanding
If Cursor misbehaves:
- remove long explanations
- break rules into two or three files
- tighten activation triggers
Simple rules outperform complex ones.
4.3 Use a Fallback Rule
A global fallback prevents unexpected behavior:
When no specific rule applies, follow core engineering standards.Production-Ready Rule Examples from This Cursor AI Guide
These examples can be used directly in your project or repurposed for your blog.
5.1 Core Engineering Rule (Recommended in This Cursor AI Guide)
# rule: Core Engineering Standards
instructions:
- Write maintainable, readable, and convention-driven code.
- Prefer clarity over cleverness.
- Always include automated tests for new logic.
- Avoid new dependencies unless necessary.
priority: 105.2 Backend Rule (Rails Example from This Cursor AI Guide)
# rule: Rails Controller Standards
apply_when:
- file_matches: "app/controllers/**/*.rb"
instructions:
- Use strong parameters for all input.
- Wrap multi-step DB operations in transactions.
- Structure JSON responses consistently.
- Add request specs covering success and error cases.
priority: 405.3 Security Rule (High Priority Guidance from the Cursor AI Guide)
# rule: Security Requirements
instructions:
- Validate and sanitize all external inputs.
- Never log or expose sensitive data.
- Use environment variables for all secrets.
- Avoid revealing internal error details in responses.
priority: 100
Advanced Rule Design Patterns in This Cursor AI Guide
As your project matures, introduce advanced strategies to maintain architectural integrity.
6.1 Layered Architecture Rules Explained in This Cursor AI Guide
Enforce strict modularity:
- Controllers do not contain business logic
- Services must be stateless and testable
- Repositories handle all data access
This ensures Cursor never produces anti-pattern code.
6.2 Tech Stack–Specific Guidance from the Cursor AI Guide
Add rules based on your tech stack:
Frontend
- Atomic design for React
- Enforce Tailwind utility patterns
- Prevent inline JavaScript in Vue templates
Backend
- Rails: prefer service objects + concerns
- Node: module boundaries and error handling patterns
API
- Consistent response envelopes
- Mandatory error codes
- Versioning conventions
6.3 Documentation Integration in a Professional Cursor AI Guide
Link rules directly to internal docs:
Refer to architecture.md for layering rules.Cursor will index these references and follow them.
Rule Governance: Keeping Your Rules Future-Proof
Long-term success relies on governance, not just writing rules.
7.1 Quarterly Rule Review
Set calendar reminders to revisit:
- code style changes
- architectural updates
- outdated instructions
7.2 Versioning for Major Rule Updates
When rules change significantly:
- create v1, v2, v3
- introduce a changelog
- communicate changes to your team
7.3 Deprecation Strategy
Mark outdated rules:
# deprecated: will be removed in Q3This prevents confusion during transitions.
Conclusion
Cursor AI Rules are more than a productivity enhancement — they are an engineering force multiplier. When configured correctly, they enforce architecture, improve code quality, guide consistent test coverage, and streamline collaboration.
Most guides stop at the basics.
This one equips you with the real-world setup, structure, workflow, and governance practices that make rules reliable and scalable.
Cursor AI Rules vs PromptXL: Which Platform Accelerates Modern Development?
Cursor AI offers a powerful rules engine that improves structure, consistency, and code quality. But when developers need faster end-to-end application generation and multi-model intelligence, a more capable prompt-driven platform becomes essential.
This is where PromptXL extends beyond traditional rule-based prompting.
How PromptXL Handles Prompts More Intelligently
Here is a clear comparison of how both tools support developers:
| Feature | Cursor AI | PromptXL |
|---|---|---|
| Follows Structured Prompting Rules | ✔ Yes | ✔ Yes |
| Multi-LLM Support (Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini) | ✖ No | ✔ Yes |
| Full-Stack App Generation | ✖ Limited | ✔ Complete UI + Backend |
| Smart Prompt Templates | Limited | ✔ Built-in |
| Prompt Memory + Workflow Context | Basic | ✔ Advanced |
| Multi-File Reasoning | Partial | ✔ Deep, Project-Wide |
| Integrated Design + Code Generation | ✖ No | ✔ Yes |
| Automatic Documentation | Limited | ✔ Included |
PromptXL evaluates prompts not only at the code level, but across the entire application layer, including:
- UI and component structure
- Backend architecture
- Database schema design
- API planning
- Test generation
- Documentation and workflow context
Instead of producing isolated edits, PromptXL turns well-written prompts into complete, structured applications.
Why Developers Add PromptXL to Their Workflow
Developers choose PromptXL because it delivers capabilities that go beyond Cursor’s rule system:
✔ Generate production-ready features in minutes
✔ Create UI, backend, documentation, and tests automatically
✔ Switch between multiple top AI models with a single click
✔ Reduce manual scaffolding, boilerplate, and design overhead
✔ Accelerate full-stack development for startups, solo builders, and enterprise teams
PromptXL doesn’t replace Cursor — it amplifies it.
Cursor provides rule-driven accuracy.
PromptXL delivers end-to-end creation speed.
Together, they form a powerful AI development environment.
🚀 Build Faster and Smarter with PromptXL
PromptXL transforms structured prompts into complete, scalable applications — from layout to logic to deployment.
PromptXL — Build smarter. Ship faster. Create without limits.
Related Topic : Cursor AI Editing Rules Explained (2026 Guide)

